Video segments from: SMC Generator
The visitor pattern is useful when we want a behavior in a hierarchy, but we don’t want to add methods to the hierarchy in order to achieve the behavior.
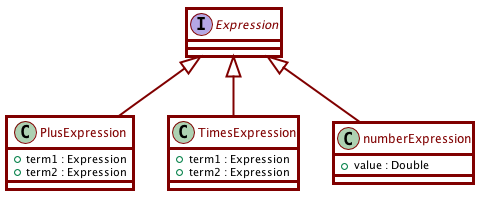
Example: Imagine an Expression superclass/interface that presents arithmetic expressions. It has subclasses like PlusExpression, TimesExpression, NumberExpression. For example the expression 4 + 5 would be presented as a PlusExpression object, whose term1 entry would be a NumberExpression object containing the value 4, and its term2 entry would be a NumberExpression object containing the value 5.

We want to do numerous operations on objects of type Expression:
But we do NOT want to keep adding new methods to the Expression interface every time we come up with a new idea. So we need to have some other class for each of these responsibilities, and that other class needs to somehow traverse the expression hierarchy. The fancy way of saying this is that we can “add polymorphic behaviors to an existing hierarchy without changing the hierarchy”.
Solution 1 (type checks and typecasts):
class Calculator {
double calculate(Expression e) {
if (e instanceof NumberExpression) {
return ((NumberExpression) e).value;
} else if (e instanceof PlusExpression) {
PlusExpression ePlus = (PlusExpression) e;
return calculate(ePlus.term1) + calculate(ePlus.term2);
} else if (e instanceof TimesExpression) {
...
}
}
}Problems with this approach:
Solution 2 (observer, part 1):
class NumberExpression {
...
void accept(Visitor v) { v.visitNumber(this); }
}
class PlusExpression {
...
void accept(Visitor v) { v.visitPlus(this); }
}
...
interface Visitor {
void visitNumber(NumberExpression e);
void visitPlus(PlusExpression e);
void visitTimes(PlusExpression e);
}
class Calculator implements Visitor {
void visitNumber(NumberExpression e) {
return e.value;
}
void visitPlus(PlusExpression e) {
return e.term1.accept(this) + e.term2.accept(this);
}
void visitTimes(TimesExpression e) {
return e.term1.accept(this) + e.term2.accept(this);
}
}Timings: