Classes and objects are the two main aspects of object oriented programming. A class defines a new data type, whereas an object is an instance of a particular class. Objects store their data in fields defined by the object’s class. Objects also have functionality that can be activated by calling the methods that belong to its class.
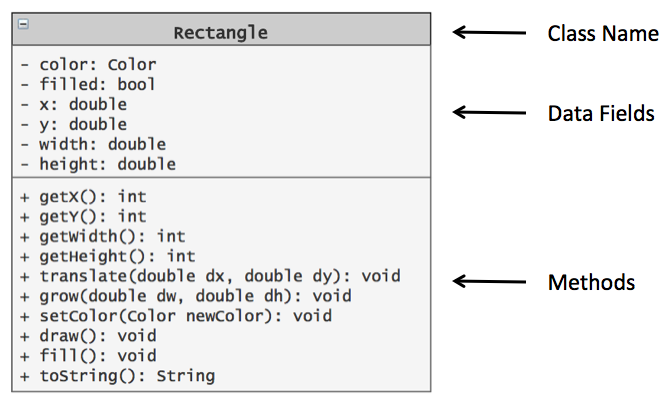
A UML diagram is a graphical summary of the data and methods in a class. Below is the UML diagram for the Rectangle class from the Simple Java Graphics library written by Cay S. Horstmann.

Identify one example of a data field for the Rectangle class from the above UML diagram.
Identify one example of a Rectangle class method that takes no arguments.
Identify one example of a Rectangle class method that takes one or more parameters.
Imagine that you have a code segment that creates a rectangle (rect1) with the following values for each of its fields:
Give the code to do each of the following to rect1
rect1 to color Violet.rect1.rect1 by 100 units and the height by 200 units.rect1.What values do you think will be returned by part d?
There is something unusual about those get... methods compared to the fields they correspond to, what is that?
Terminology Note
A method should do one thing, either provide access to object data values or mutate data values. Never both (with some exceptions)!